Background
Modern opto-electronic devises are based on semiconductor hetero- structures employing the process of electron-hole pair annihilation. In particular polar materials enable to create a variety of classic and even quantum light sources. However, the key challenge – the inherent electrical crystal polarization of such materials – remains unsolved and thus deteriorates the electron-hole pair annihilation rate. The invention presented here introduces a new approach to adjusting those polarization effects. It marks the onset of an entire new class of ultra-fast and efficient devices based on any polar material.
Technical Description
Former research in this field had focused on less-polar crystal planes or even on the stabilization of unnatural phases, but never was able to gain industrial maturity. The new approach introduces a sequence of reverse interfaces to compensate for these polarization effects, while the natural polar crystal growth direction is maintained. This specific approach is provoking a boost in the performance of the device. This approach allows for an adaptation in all established industrial processes, while the polarization becomes adjustable, even below zero.
As a result, not only the radiative exciton decay rates are being significantly increased, even so the electric potential as a tunable parameter could be established. Hence we soon can expect the creation of, e.g. (quantum-) light sources based on polar heterostructures. The optical signatures of such light sources are decoupled from the detrimental effects of crystal polarization.
Possible Applications
The system can be used in edge emitting lasers, in LEDs, in single photon sources with various wave lengths or in any other (quantum-) light sources.
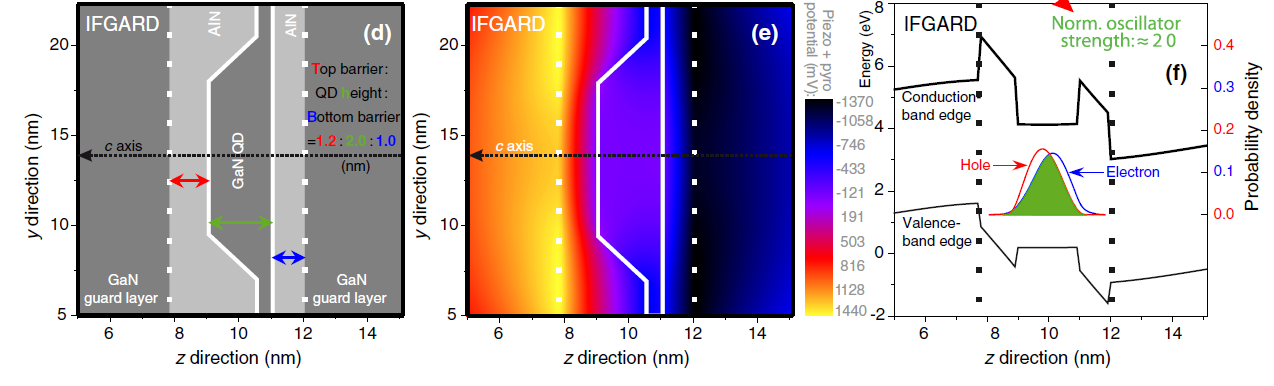
QD (quantum dots) structure comprising the IFGARD. d) Layer sequence of 2d scan, e) contourplots of sum of the piezo- and pyroelectric potential, f) evidence of constant potential shown in the band-edge scans along the c-axis through the QD center