


This invention enables the production of tailor-made extruded profiles for the forming of metals, for example in the production of pipes and the like. The process can be used in the automotive or aerospace industries.


This Invention enables an improved catalysis of commonly used reactions in fuel cells and electrolyzers as well as an easier manufacturing process for this catalyst material.


Novel methods for the large-scale production of basic chemicals must not only be energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, but should also increasingly prevent undesirable by-products or ideally even convert them into useful resources. The advantages of the reaction process according to the invention can be applied to all alkenes and polyenes in order to produce basic chemicals and bind CO2 in the process.



This new type of liquid distributor is used, for example, in absorption chillers and can replace systems that were previously more complex and more susceptible over the operating time.



With the increasing share of wind energy in electrical energy systems, increased grid frequency fluctuations occur due to varying wind speeds. In regions or grids with strongly fluctuating wind supply and high wind energy penetration, the invention makes it possible to feed a high proportion of renewable energy into the grid while still ensuring grid stability.
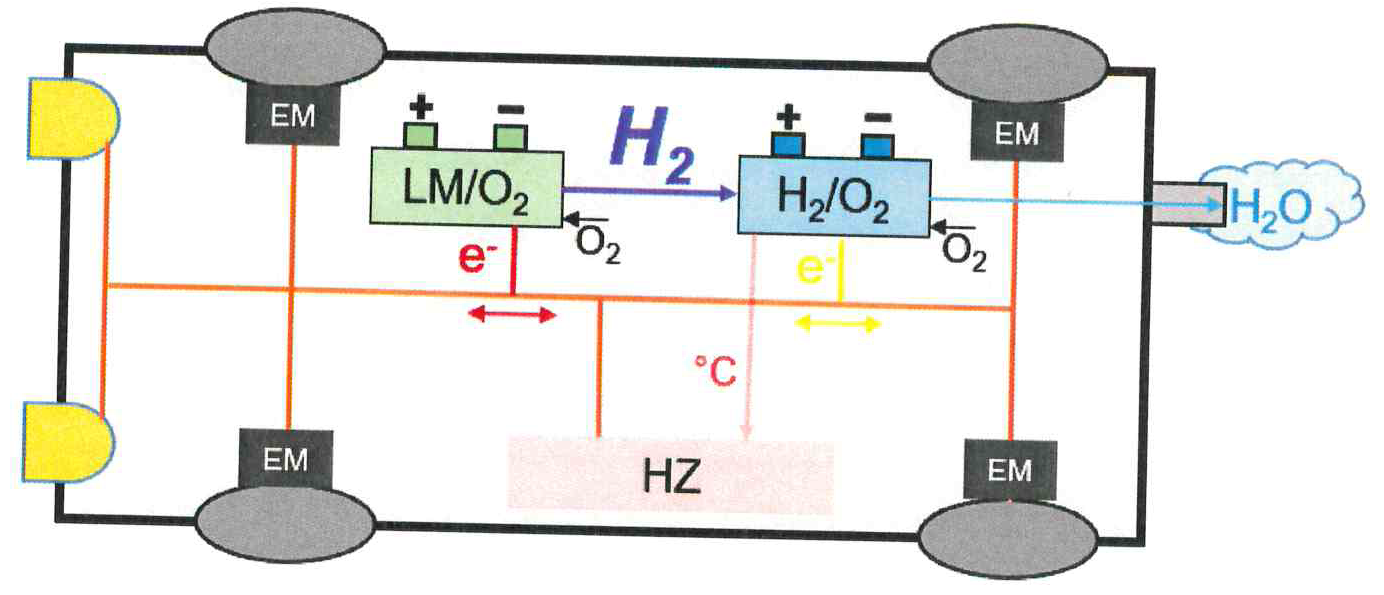


In conventional light metal-air batteries (LMB), hydrogen production has a performance-reducing effect and should therefore be avoided wherever possible. This invention will use the hydrogen for combining a light metal foam air battery (LMSLB) with a fuel cell.
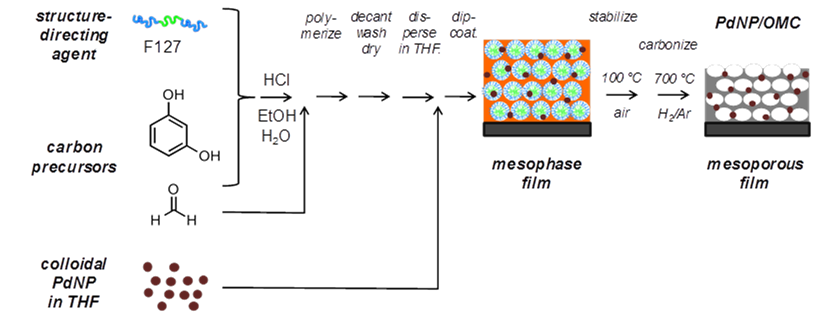


Production method for mesoporous carbon coatings incorporating noble metal nano particles.
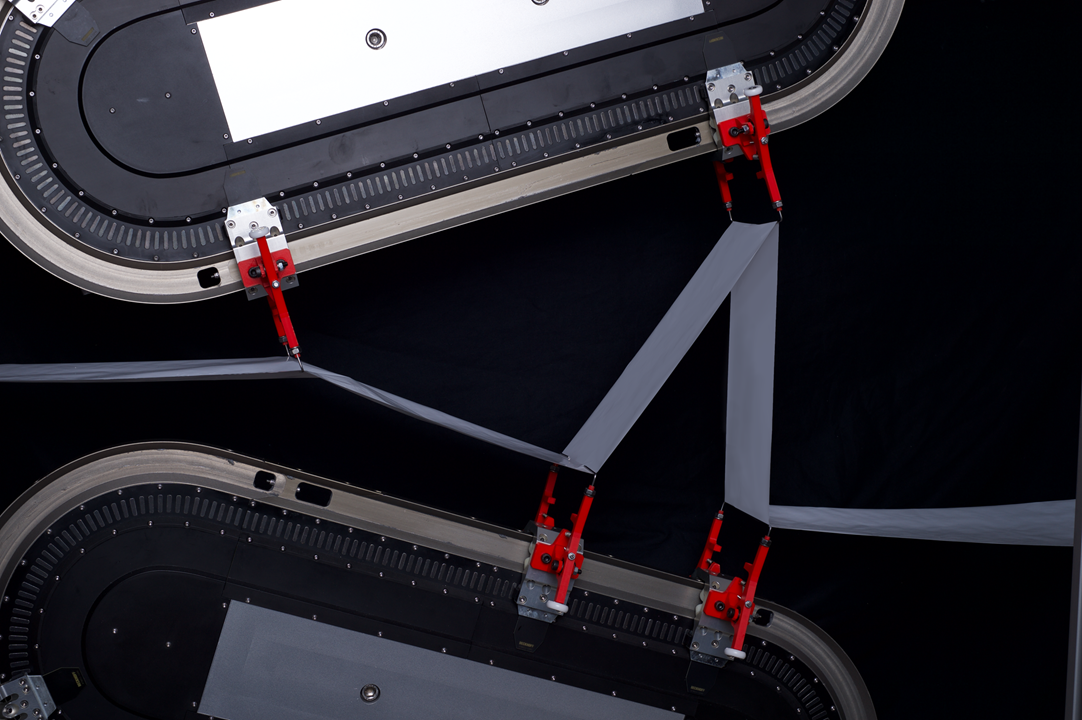


The Invention enables the continuous Z-folding of a electrode-seperator-composite for faster and cost-efficient production of battery-cells.
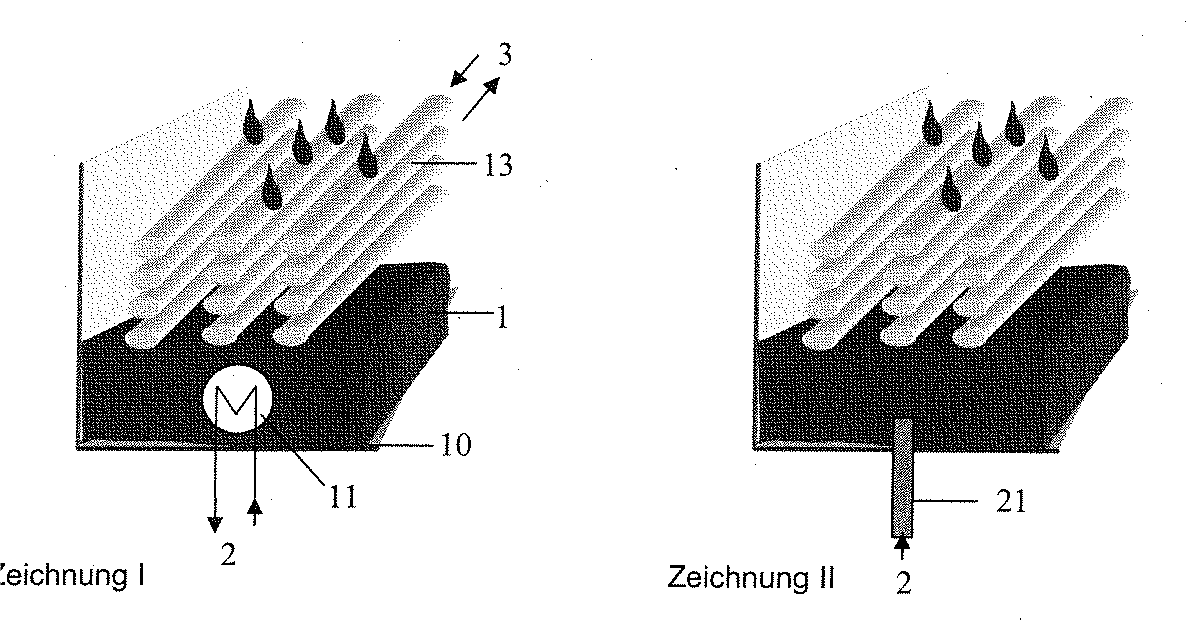


This invention offers a novel technology to increase the efficiency of cooling systems.
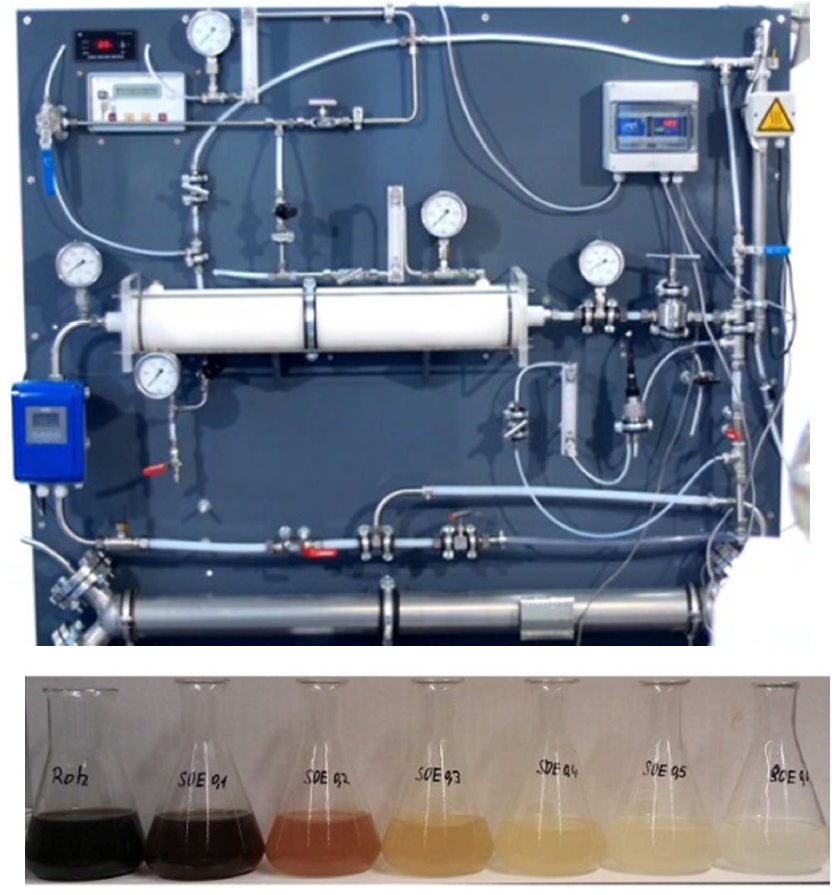



This invention provides a way to purify wastewater from synthetic substances as well as bacteria or viruses.
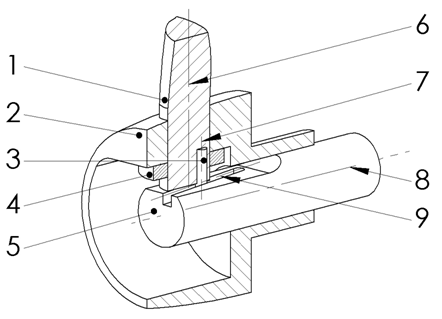


This invention provides a control method for wind turbines to adapt their overall performance to the prevailing operating conditions.



Thermally driven absorption heat pumps with ionic liquids have a low intensity of heat release, which results in high costs for heat transfer. The intensity of the heat release is significantly influenced by the mass transfer that takes place on the surface of a fluid film through diffusion. The invention have been solved such difficulties and achieve heat flow densities of up to 5 kW/m² with comparatively low driving forces.
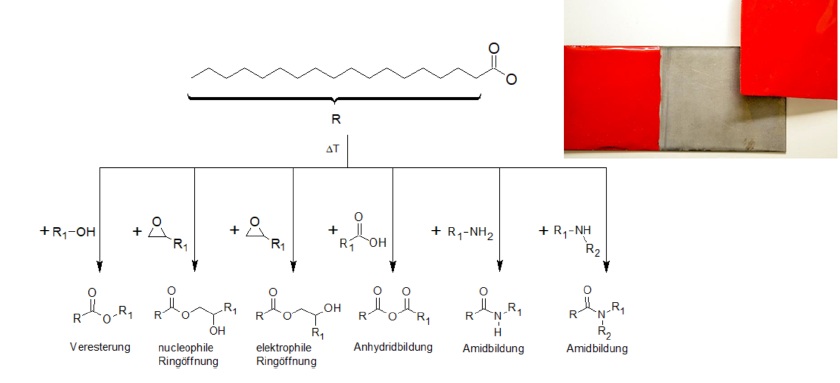


The invention describes a process for recycling powder coating waste in which the adhesion-promoting functional groups of the powder coatings are chemically inactivated by adding a surfactant. This allows powder coating waste to be thermally processed without sticking to metal surfaces, e.g. by extrusion or injection moulding, and used as a high-quality raw material in recycling processes or other applications.
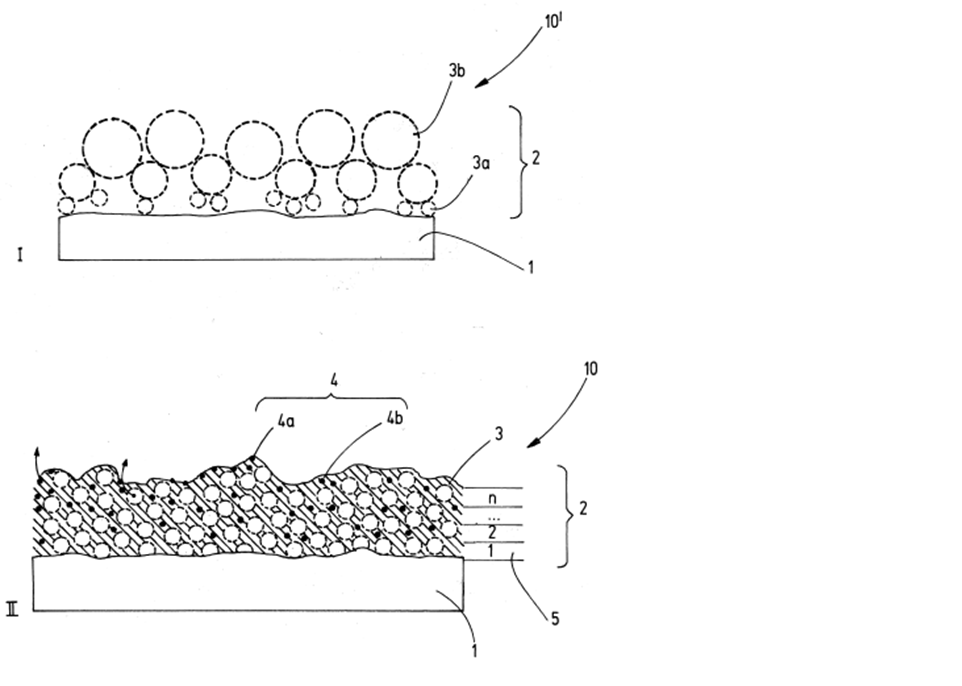


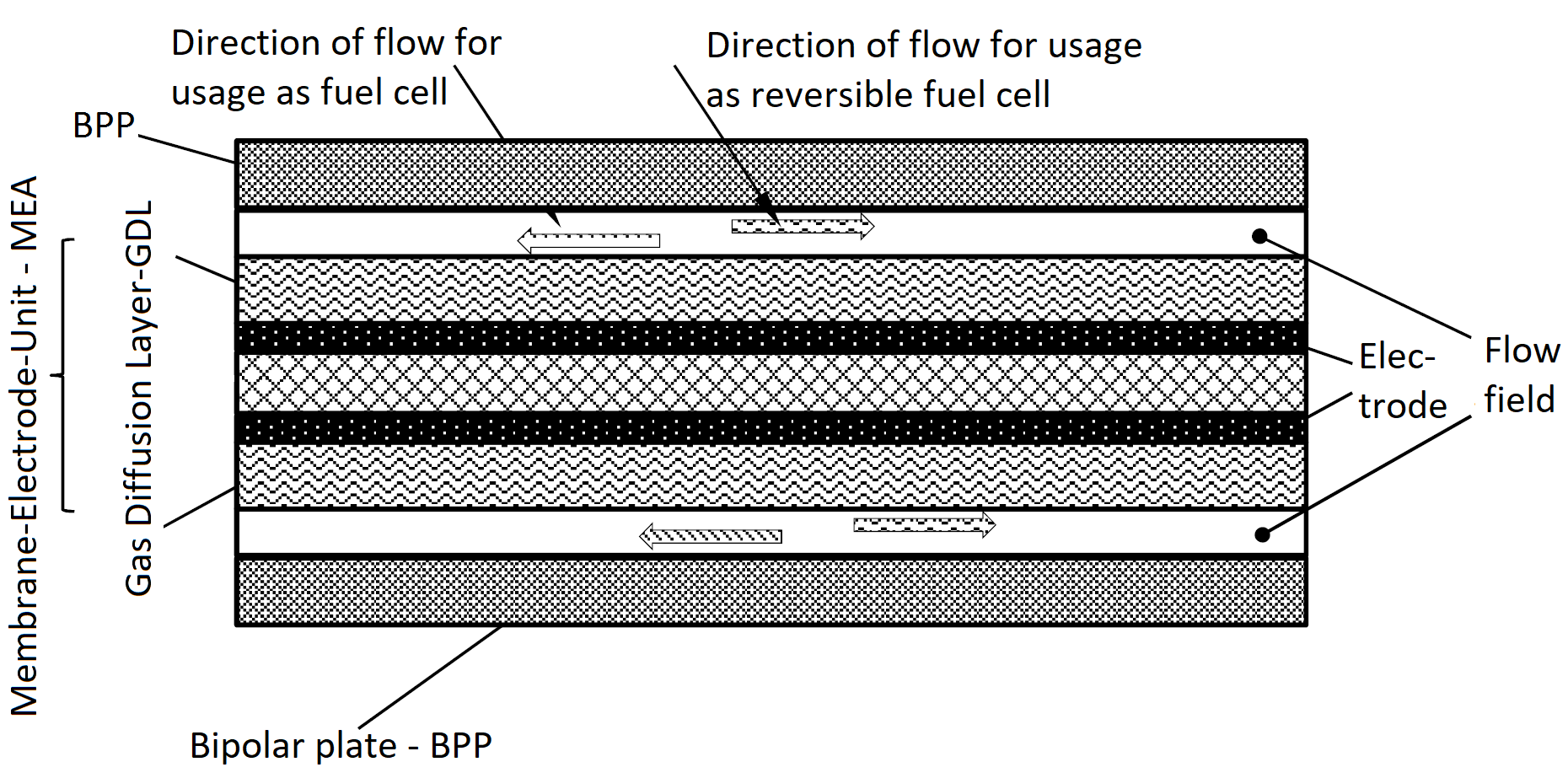
An enhanced electrode for fuel cells and electro catalysis and the manufacturing process needed.
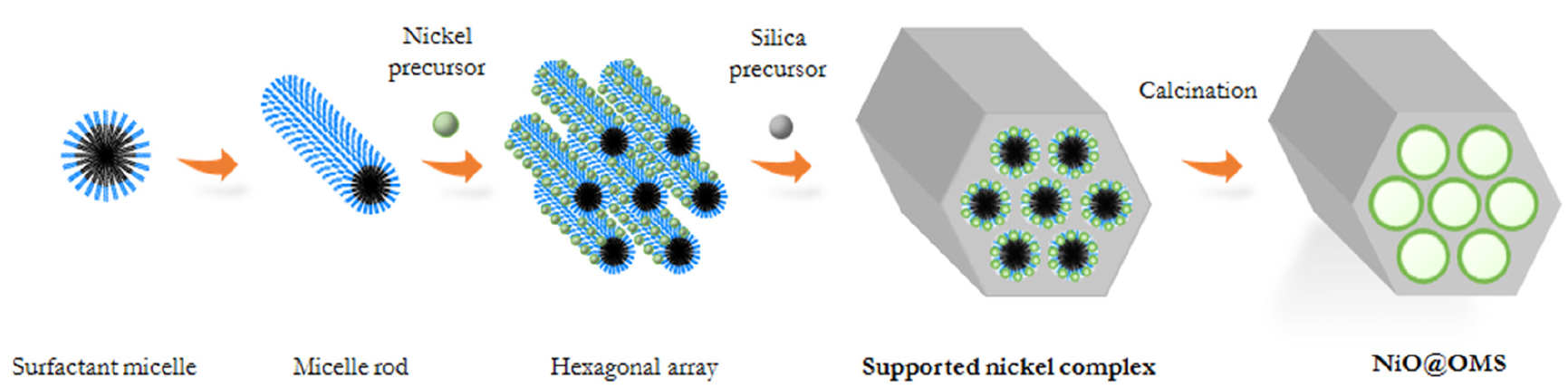


This invention enables an easier production of ordered mesoporous silica structures even at room temperature.
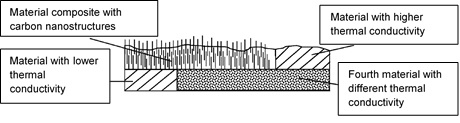


Wherever heat is generated in electronic components as a result of power loss, this must also be dissipated in order to prevent the components from overheating. The invention relates to a method for producing a composite material (metals and carbon), a composite material and a use of the composite material as a heat conductor as well as a heat exchanger. It enables an increase in the interface area and/or contact area of a redetachable and reusable thermal interface, thereby increasing the heat flow between two surfaces.
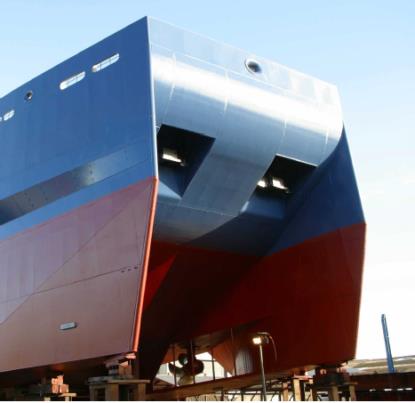



With the invention of the SOS system, it is possible to skim oil slicks from the surface of the water, i.e. to absorb them, even in heavy seas.
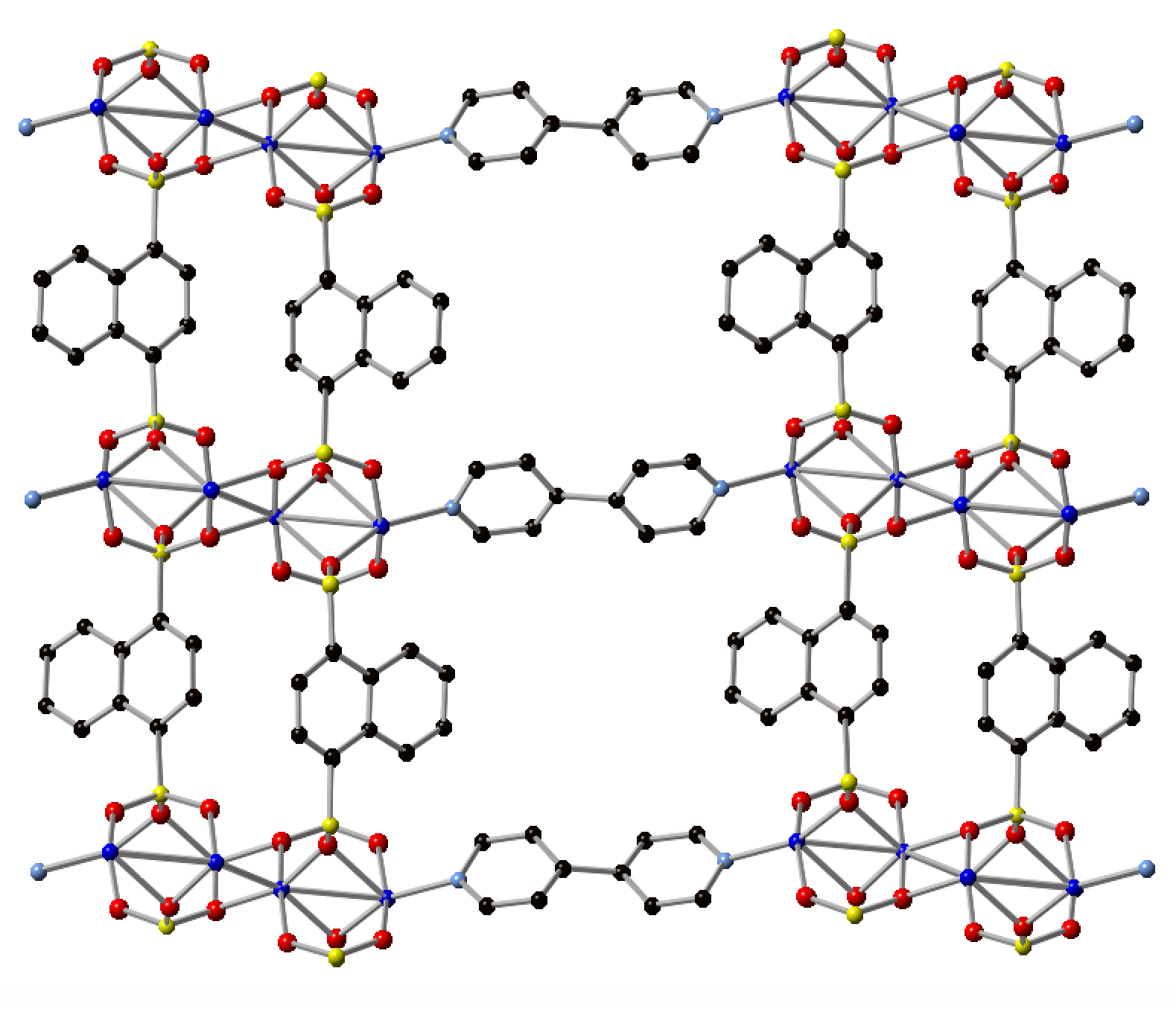


This Invention describes the usage of a novel semiconductor MOF comprising Phosphonate and Arsenate for a novel electrode material used in super capacitors.
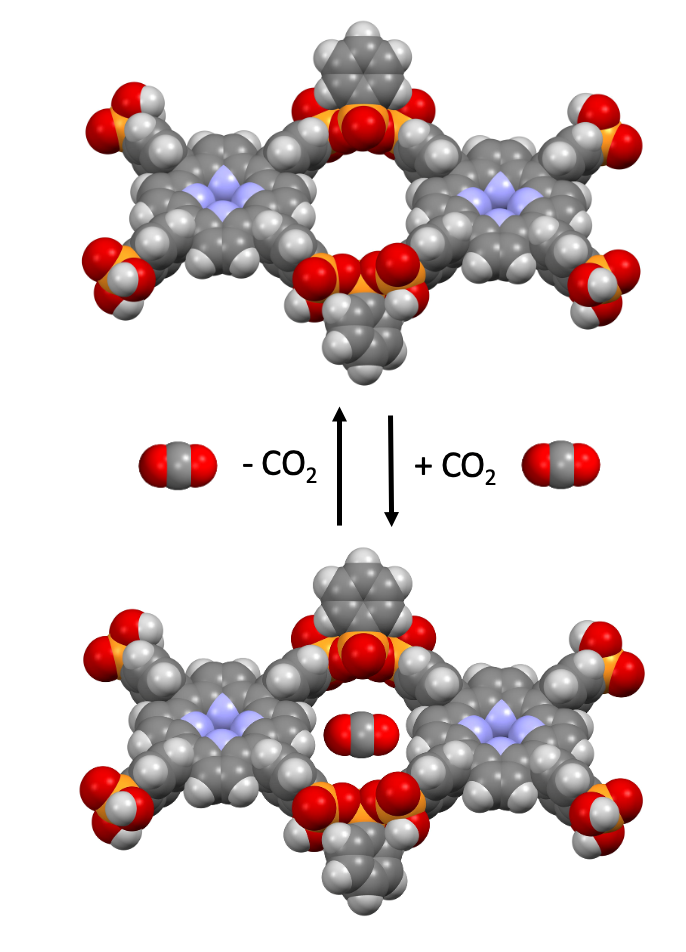


The invention discloses a new class of hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks (HOFs) built from organic linkers containing a hydroxyl group and a tetrahedral central atom. These HOFs uniquely combine semiconductive and proton-conductive properties with adjustable porosity and high thermal stability. They do not require metals, are environmentally friendly, and are suitable for advanced energy and electronic applications.
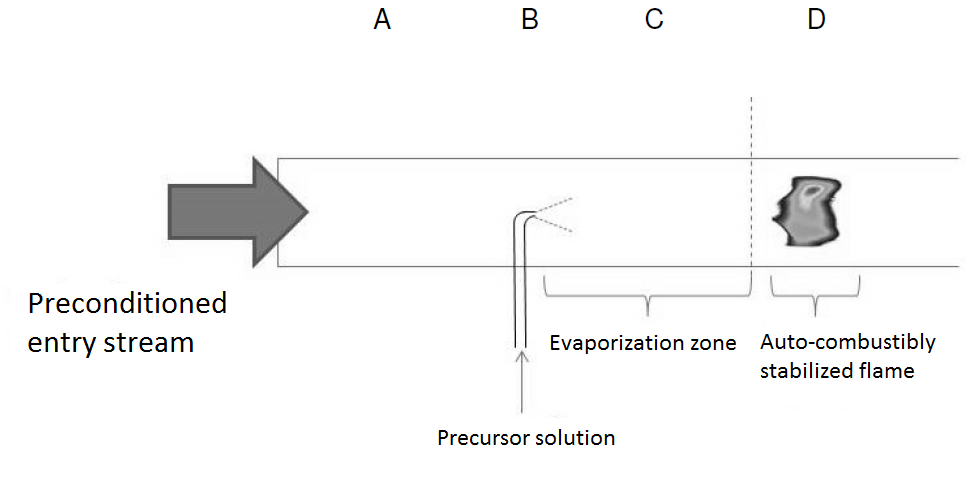


This process enables the generation of nanoparticles in spray flames which can be used, for example, as coating material, in electrical devices, for thermal conduction or insulation or as catalyst.
The Center for Intellectual Property (ZfgE) at the TU Berlin is the central point of contact for all topics relating to intellectual property law and intellectual property.
We patent and market the inventions of the TU Berlin, and we also teach and research technical and intellectual property law.
This makes us the central contact for inventors of the TU Berlin, for cooperation partners from industry and science as well as for interested scientists and experts from the fields of technology and law.
Zentrum für geistiges Eigentum
Technische Universität Berlin
Straße des 17. Juni 135
10623 Berlin